Effortless Setup: Instantly deploy your entire Linux toolkit in one click

I'm use with the same fundamental stack to build Linux servers : Docker, Docker compose, Portainer and homepage. But, being a bit lazy, I dread the manual installation every time.
So, I had a lightbulb moment— why not script the whole thing?
So, as an old magician once said : ✨
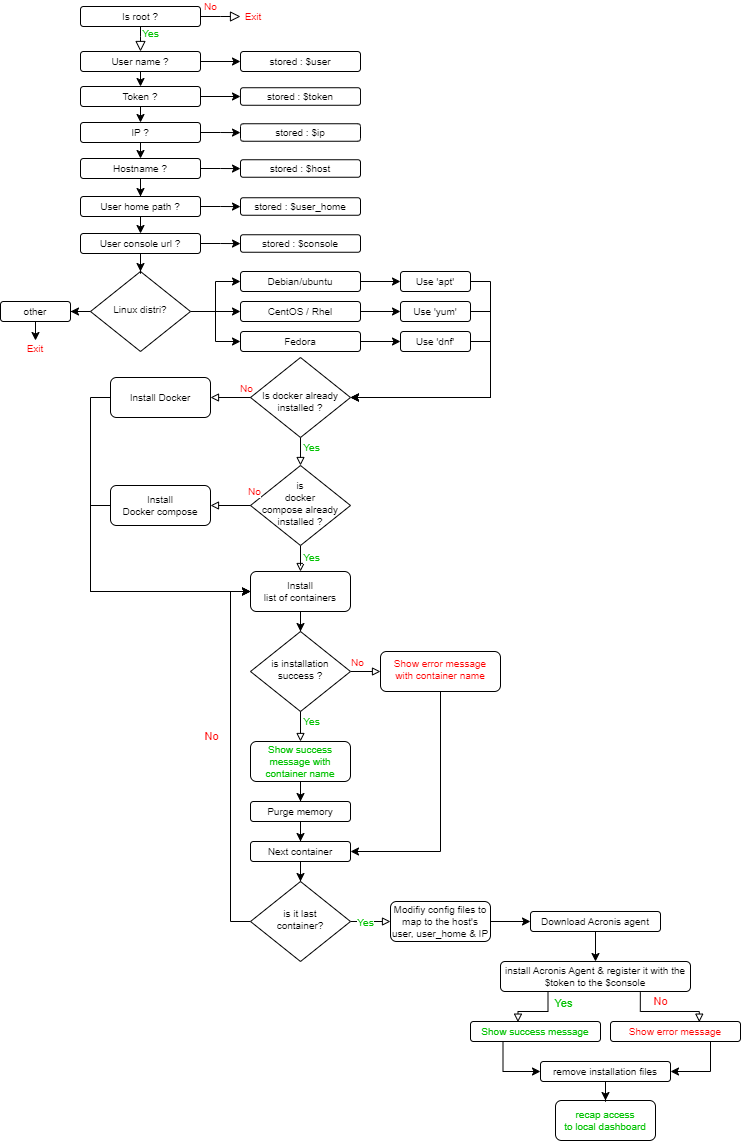
The flow process diagram of this script
let's bash !
I whipped up a bash script to install all the necessary tools and tweak the configuration files to fit the current server.
First things first, let’s make sure the script is running as root.
if [ "$EUID" -ne 0 ]; then
echo -e "${RED}You should be root to run that script. Use sudo.${NC}"
exit 1
ficheck if it run as root
Pass the variables as arguments in the command or retrieve them directly from the system.
- Linux User (for installation path)
- Acronis token
- Acronis Cloud URL
- Host IP
- Hostname
# Default values
user=""
token=""
cloud=""
# Parse it
for arg in "$@"
do
case $arg in
--user=*)
user="${arg#*=}"
shift
;;
--token=*)
token="${arg#*=}"
shift
;;
--cloud=*)
cloud="${arg#*=}"
shift
;;
*)
;;
esac
done
# Check if parms are provided
if [ -z "$user" ] || [ -z "$token" ] || [ -z "$cloud" ]; then
echo "Usage: $0 --user=<username> --token=<token> --cloud=<cloud>"
exit 1
fi
# Get IP address
IP=$(hostname -I | awk '{print $1}')
# Get hostname
host=$(hostname)Get the parameters
Next, we’ll check which Linux distribution the script is running on. This allows us to select the appropriate package manager—apt, yum, or dnf to install Docker and Docker compose.
# Linux distr detect
if [ -f /etc/os-release ]; then
. /etc/os-release
else
echo -e "${RED}\nUnsupported Linux distribution !\n${NC}"
exit 1
fi
# Install docker function
install_docker() {
if [ "$ID" == "ubuntu" ] || [ "$ID" == "debian" ]; then
apt-get update
apt-get install -y apt-transport-https ca-certificates curl software-properties-common gnupg
curl -fsSL https://download.docker.com/linux/$ID/gpg | apt-key add -
add-apt-repository "deb [arch=$(dpkg --print-architecture)] https://download.docker.com/linux/$ID $(lsb_release -cs) stable"
apt-get update
apt-get install -y docker-ce
elif [ "$ID" == "centos" ]; then
yum install -y yum-utils device-mapper-persistent-data lvm2
yum-config-manager --add-repo https://download.docker.com/linux/centos/docker-ce.repo
yum install -y docker-ce
systemctl start docker.service
systemctl enable docker.service
elif [ "$ID" == "fedora" ]; then
dnf -y install dnf-plugins-core
dnf config-manager --add-repo https://download.docker.com/linux/fedora/docker-ce.repo
dnf install -y docker-ce
systemctl start docker.service
systemctl enable docker.service
else
echo -e "${RED}\nUnsupported Linux distribution !\n${NC}"
exit 1
fi
}
# Install docker compose function
install_docker_compose() {
COMPOSE_VERSION=$(curl -s https://api.github.com/repos/docker/compose/releases/latest | grep '"tag_name":' | sed -E 's/.*"([^"]+)".*/\1/')
curl -L "https://github.com/docker/compose/releases/download/${COMPOSE_VERSION}/docker-compose-$(uname -s)-$(uname -m)" -o /usr/local/bin/docker-compose
chmod +x /usr/local/bin/docker-compose
}
check the correct package manager
Next step is to check if Docker and Docker compose are already installed in the current system.
-> If not, then install them, if yes skip them.
# Check if Docker is install
if ! command -v docker &> /dev/null
then
echo -e "${WHITE}Can't find Docker. Installing Docker...${NC}"
install_docker
echo -e "${GREEN}Docker sucessfully installed.${NC}"
else
echo -e "${GREEN}Docker is already installed.${NC}"
fi
# Check if Docker compose is install
if ! command -v docker-compose &> /dev/null
then
echo -e "${WHITE}Docker Compose is not installed. Installing Docker Compose...${NC}"
install_docker_compose
echo -e "${GREEN}Docker Compose sucessfully installed.${NC}"
else
echo -e "${GREEN}Docker Compose is already installed.${NC}"
fi
Check if Docker/Docker compose are already installed, and then install if not
Following by installing Portainer in order to make management of container easiest.
echo -e "${WHITE}\nInstallation and run of container 'portainer-ce'...${NC}"
if docker volume create portainer_data && \
docker run -d -p 8000:8000 -p 9000:9000 --name portainer --restart=always \
-v /var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock \
-v portainer_data:/data portainer/portainer-ce; then
echo -e "${NC}Waiting for the container to start ....${NC}"
# Wait for 10s
for i in {1..10}; do
sleep 1
echo -ne "${WHITE}Loading: $((i * 10))%\r${NC}"
done
echo -ne '\n'
# result
echo -e "${GREEN}The container 'portainer-ce' has been installed and run successfuly. Go to http://$IP:9000 to see the interface.\n${NC}"
sync; echo 3 > /proc/sys/vm/drop_caches
else
echo -e "${RED}\nFailed to install or launch container 'portainer-ce'.\n${NC}"
fiinstallation of Portainer
the curent line "sync; echo 3 > /proc/sys/vm/drop_caches" is to manage memory consomption on small server during installation process.
Now, you can loop each container you want to install using "Docker run"
Here is as an example a loop of 2 containers :
#container1
echo -e "${WHITE}Installing and launching containers... ${NC}"
if docker run -d --restart unless-stopped --name snippet-box -p 8020:5000 -v /home/$user/snippet-box:/app/data pawelmalak/snippet-box:latest; then
echo -e "${NC}Waiting for the container to start ....${NC}"
for i in {1..10}; do
sleep 1
echo -ne "${WHITE}Loading: $((i * 10))%\r${NC}"
done
echo -ne '\n'
echo -e "${GREEN}The container 'pawelmalak/snippet-box' has been installed and run successfuly. Go to http://$IP:8020 to see the interface.\n${NC}"
sync; echo 3 > /proc/sys/vm/drop_caches
else
echo -e "${RED}Failed to install or launch container 'pawelmalak/snippet-box'.${NC}"
fi
#container2
if docker run -d --restart unless-stopped --name it-tools -p 8010:80 -v /home/$user/it-tools:/app/data corentinth/it-tools:latest; then
echo -e "${NC}Waiting for the container to start ....${NC}"
for i in {1..10}; do
sleep 1
echo -ne "${WHITE}Loading: $((i * 10))%\r${NC}"
done
echo -ne '\n'
echo -e "${GREEN}The container 'corentinth/it-tools' has been installed and run successfuly. Go to http://$IP:8010 to see the interface.\n${NC}"
sync; echo 3 > /proc/sys/vm/drop_caches
else
echo -e "${RED}Failed to install or launch container 'corentinth/it-tools'.${NC}"
fimultiple containers deployment
Here’s the list of containers I usually deploy using this script :
- pawelmalak/snippet-box
- corentinth/it-tools
- kanboard/kanboard
- jgraph/drawio
- neosmemo/memos
- zadam/trilium
- lucabelluccini/commafeed-docker
- frooodle/s-pdf
- lscr.io/linuxserver/changedetection.io
- wbsu2003/tldraw
- louislam/uptime-kuma
- m4yur/mindmaps
Then, I deploy "ghcr.io/gethomepage/homepage" as a dashboard in order to have access to all container easily.
if docker run -d --name=homepage -e PUID=1000 -e PGID=1000 -p 80:3000 -v /home/$user/homepage:/app/config -v /var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock:ro --restart unless-stopped ghcr.io/gethomepage/homepage; then
echo -e "${NC}Waiting for the container to start ....${NC}"
for i in {1..10}; do
sleep 1
echo -ne "${WHITE}Loading: $((i * 10))%\r${NC}"
done
echo -ne '\n'
echo -e "${GREEN}The container 'ghcr.io/gethomepage/homepage' has been installed and run successfuly. Go to http://$IP to see the interface.\n${NC}"
sync; echo 3 > /proc/sys/vm/drop_cachesHomepage container for fire-up a dashboard to rules them all
Once the container is deployed, we need to update the configuration files to match the current server's IP address and make some cosmetic adjustments.
this first section download tailored files on my own to replace the one used by the homepage container :
echo -e "${NC}Downloading SEtool configuration files...${NC}"
curl -L "https://my-donwload-server/bookmarks.yaml" -o /home/$user/homepage/bookmarks.yaml
curl -L "https://my-donwload-server/services.yaml" -o /home/$user/homepage/services.yaml
curl -L "https://my-donwload-server/settings.yaml" -o /home/$user/homepage/settings.yaml
curl -L "https://my-donwload-server/widgets.yaml" -o /home/$user/homepage/widgets.yamldownload the config files
Refer to the documentation of homepage to tailor theses files as you which.
Then, the new settings are modified to be mapped with the correct IP address by replacing "myip" character chain with the current IP.
awk -v ip="$IP" '{gsub(/myip/, ip); print}' /home/$user/homepage/bookmarks.yaml > /home/$user/homepage/bookmarks.yaml.tmp && mv /home/$user/homepage/bookmarks.yaml.tmp /home/$user/homepage/bookmarks.yaml
Set current IP to the settings of the dashboard
last step is to install Acronis agent to backup this new server.
let's check if Acronis is already installed or not by checking if aakore service is running on the server :
if pgrep -x "aakore" > /dev/null; then
echo -e "${GREEN}Acronis agent is already running. No installation is needed${NC}"
else
install_acronis_agent
fiis Acronis service running on the server ?
then if not, let install Acronis agent and register it to my Cloud console using "install_acronis_agent" function :
install_acronis_agent() {
# Download agent
echo -e "${GREEN}Installing Acronis agent, downloading binary...${NC}"
wget -O /tmp/AcronisCyberProtectAgentForLinux.bin "https://my-download-server/AcronisCyberProtectAgentForLinux.bin"
# Make it executable
chmod +x /tmp/AcronisCyberProtectAgentForLinux.bin
# Install agent
echo -e "Installing Acronis agent..."
/tmp/AcronisCyberProtectAgentForLinux.bin -i BackupAndRecoveryAgent -a --rain=https://$cloud --token=$token
# Check if the installation was successful
if pgrep -x "aakore" > /dev/null; then
echo -e "${GREEN}Installation successful${NC}"
sync; echo 3 > /proc/sys/vm/drop_caches
else
echo -e "${RED}Failed to install Acronis agent${NC}"
fi
# Clean up
rm -f /tmp/AcronisCyberProtectAgentForLinux.bin
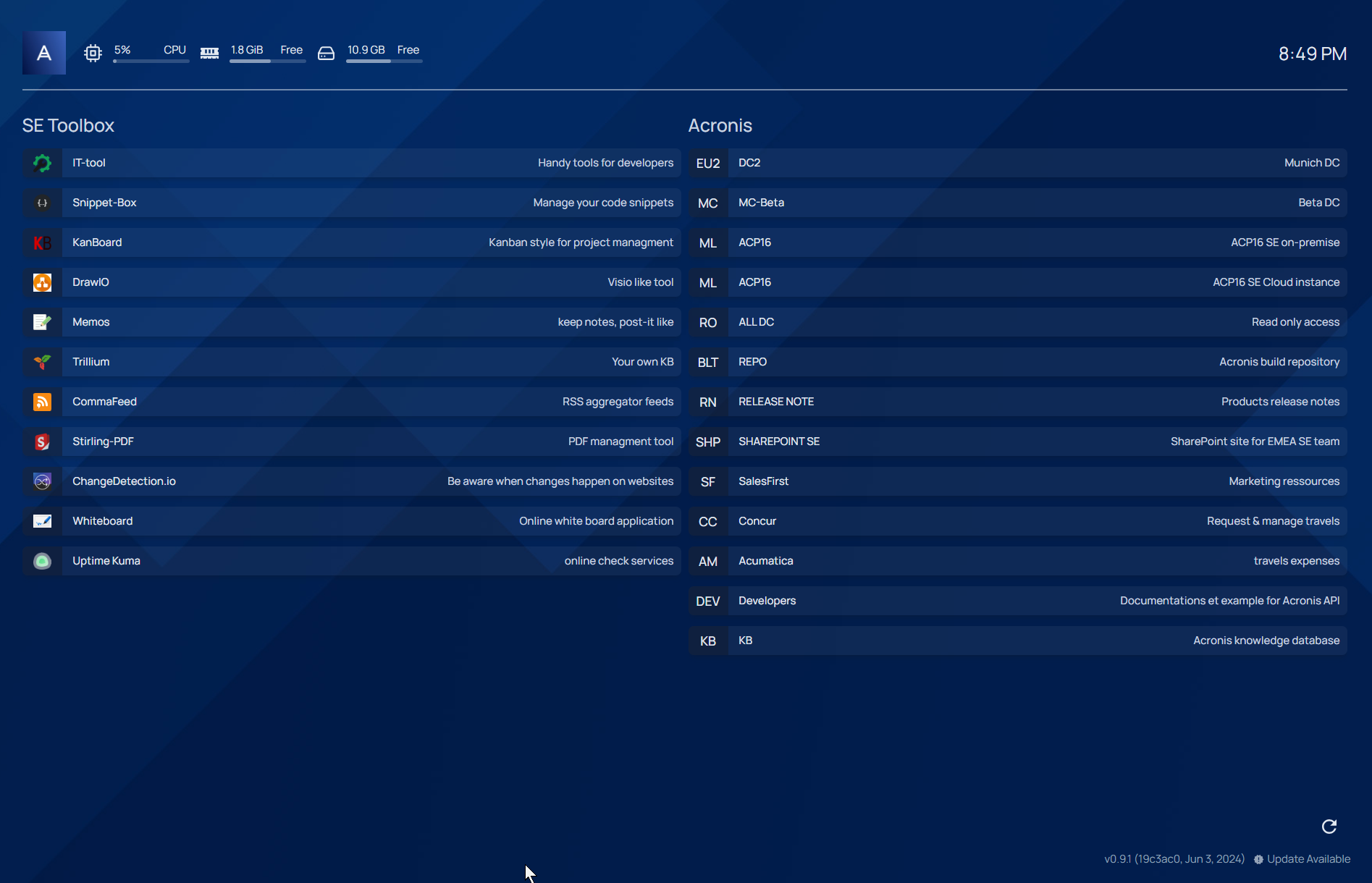
}And there you have it!
In just a few minutes, our server is fully installed and configured just the way we need it :
to run the script, don't forget to pass the needed parameters like :
./install.sh --user=<username> --token=<yourcloudtoken> --cloud=<yourcloudurl>Below the full script in zip file
and some example of config files in this Zip archive